RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS – THE CONDITION AND ITS MANAGEMENT
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common form of inflammatory arthritis, occurring throughout the world and in all ethnic groups. It is a chronic disease characterized by a clinical course of exacerbations and remissions.1
A chronic multi system disease of unknown etiology characterized by persistent inflammatory synovitis, usually involving peripheral joints symmetrically. Although cartilaginous destruction, bony erosions, and joint deformity are hallmarks, the course of RA can be quite variable. An association with HLA-DR4 has been noted; both genetic and environmental factors may play a role in initiating disease. The propagation of RA is an immunologically mediated event in which joint injury occurs from synovial hyperplasia; lymphocytic infiltration of synovium; and local production of cytokines and chemokines by activated lymphocytes, macrophages, and fibroblasts.2
Pathophysiology
 RA is a complex disease with both genetic and environmental components. The importance of genetic factors is demonstrated by higher concordance of RA in monozygotic (12–15%) compared with dizygotic twins (3%), and an increased frequency of diseasein first-degree relatives of patients. It is currently believed that RA occurs when an environmental stimulus, such as infection, triggers autoimmunity in a genetically susceptible host by modifying hosts proteins through processes like citrullination so that they become immunogenic. However, no single specific pathogen has been identified as a cause. An important environmental risk factor is cigarette smoking, which is also associated with more severe disease and reduced responsiveness to treatment. Remission may occur during pregnancy and sometimes RA first presents post-partum. This is likely to be due to suppression of the immune response during pregnancy but hormonal changes may also play a role. The disease is characterized by infiltration of the synovial membrane with lymphocytes, plasma cells, dendrite cells and macrophages. There is evidence that CD4+ T lymphocyte sand B cells play important roles in the pathogenesis of RA by interacting with other cells in the synovium. Lymphoid follicles form within the synovial membranein which T- and B-cell interactions occur, causing activation of Tcells to produce cytokines and activation of B cells to produce auto antibodies, including RF and ACPA. Synovial macrophagesare activated by TNF and interfere on gamma (IFN-γ), produced by T cells. The macrophages produce several pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF, IL-1 and IL-6, which act on synovialfibroblasts to produce further cytokines, setting up a positive feedback loop. The synovial fibroblasts proliferate, causingsynovial hypertrophy and producing matrix metalloproteinase’sand the proteinase ADAMTS-5, which degrade soft tissues and cartilage. Prostaglandins and nitric oxide produced within the inflamed synovium cause vasodilatation, resulting in swellingand pain. Systemic release of IL-6 triggers production of acute phase proteins by the liver. At the joint margin, the inflamed synovium (pannus) directly invades bone and cartilage to cause joint erosions. A key pathogenic factor in bone erosions and periarticular osteoporosis is osteoclast activation, stimulated by the production of M-CSF by synovial cells and RANKL by activated T cells. New blood vessel formation (angiogenesis) occurs, causing the inflamed synovium to become highly vascular. Within these blood vessels, pro-inflammatory cytokines activate endothelial cells, which support recruitment of yet more leucocytesto perpetuate the inflammatory process. Later, fibrous or bony ankylosis may occur. Muscles adjacentto inflamed joints atrophy and may be infiltrated with lymphocytes.This leads to progressive biomechanical dysfunction and mayfurther amplify destruction. Rheumatoid nodules occur in patients who are RF- or ACPA positive and primarily affect extensor tendons. They consist ofa central area of fibrinoid material surrounded by a palisade of proliferating mononuclear cells. Granulomatous lesions may occur in the pleura, lung, pericardium and sclera.1
RA is a complex disease with both genetic and environmental components. The importance of genetic factors is demonstrated by higher concordance of RA in monozygotic (12–15%) compared with dizygotic twins (3%), and an increased frequency of diseasein first-degree relatives of patients. It is currently believed that RA occurs when an environmental stimulus, such as infection, triggers autoimmunity in a genetically susceptible host by modifying hosts proteins through processes like citrullination so that they become immunogenic. However, no single specific pathogen has been identified as a cause. An important environmental risk factor is cigarette smoking, which is also associated with more severe disease and reduced responsiveness to treatment. Remission may occur during pregnancy and sometimes RA first presents post-partum. This is likely to be due to suppression of the immune response during pregnancy but hormonal changes may also play a role. The disease is characterized by infiltration of the synovial membrane with lymphocytes, plasma cells, dendrite cells and macrophages. There is evidence that CD4+ T lymphocyte sand B cells play important roles in the pathogenesis of RA by interacting with other cells in the synovium. Lymphoid follicles form within the synovial membranein which T- and B-cell interactions occur, causing activation of Tcells to produce cytokines and activation of B cells to produce auto antibodies, including RF and ACPA. Synovial macrophagesare activated by TNF and interfere on gamma (IFN-γ), produced by T cells. The macrophages produce several pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF, IL-1 and IL-6, which act on synovialfibroblasts to produce further cytokines, setting up a positive feedback loop. The synovial fibroblasts proliferate, causingsynovial hypertrophy and producing matrix metalloproteinase’sand the proteinase ADAMTS-5, which degrade soft tissues and cartilage. Prostaglandins and nitric oxide produced within the inflamed synovium cause vasodilatation, resulting in swellingand pain. Systemic release of IL-6 triggers production of acute phase proteins by the liver. At the joint margin, the inflamed synovium (pannus) directly invades bone and cartilage to cause joint erosions. A key pathogenic factor in bone erosions and periarticular osteoporosis is osteoclast activation, stimulated by the production of M-CSF by synovial cells and RANKL by activated T cells. New blood vessel formation (angiogenesis) occurs, causing the inflamed synovium to become highly vascular. Within these blood vessels, pro-inflammatory cytokines activate endothelial cells, which support recruitment of yet more leucocytesto perpetuate the inflammatory process. Later, fibrous or bony ankylosis may occur. Muscles adjacentto inflamed joints atrophy and may be infiltrated with lymphocytes.This leads to progressive biomechanical dysfunction and mayfurther amplify destruction. Rheumatoid nodules occur in patients who are RF- or ACPA positive and primarily affect extensor tendons. They consist ofa central area of fibrinoid material surrounded by a palisade of proliferating mononuclear cells. Granulomatous lesions may occur in the pleura, lung, pericardium and sclera.1
Clinical features
Articular Manifestations2
Typically a symmetric polyarthritis of peripheral joints with pain, tenderness, andswelling of affected joints; morning stiffness is common; proximal inter phalangeal(PIP) and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints frequently involved; joint deformitiesmay develop after persistent inflammation.
Extraarticular Manifestations2
- Cutaneous: rheumatoid nodules, vasculitis Pulmonary: nodules, interstitial disease, bronchiolitis obliterans–organizing pneumonia (BOOP), pleural disease, Caplan’s syndrome [sero (+) RA associated with pneumoconiosis]
- Ocular: keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), episcleritis, scleritis
- Hematologic: anemia, Felty’s syndrome (splenomegaly and neutropenia) Cardiac: pericarditis, myocarditis
- Neurologic: myelopathies secondary to cervical spine disease, entrapment, vasculitis
- Anorexia, weight loss and fatigue may occur throughout the disease course. Osteoporosis is a common complication and muscle-wasting may occur as the result of systemic inflammation and reduced activity.
Examination findings reveal
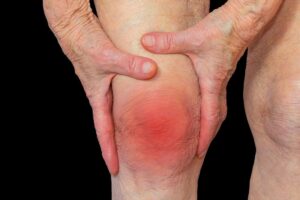
- Swelling and tenderness of the affected joints.
- Erythema is unusual and its presence suggests coexistent sepsis.
- Characteristic deformities may developwith long-standing uncontrolled disease, although these havebecome less common over recent years with more aggressive management. They include ulnar deviation of the fingers, ‘swanneck’ deformity, the boutonnière or ‘button hole’ deformity, anda Z deformity of the thumb). Dorsal subluxation ofthe ulna at the distal radio-ulnar joint may occur and contributeto rupture of the fourth and fifth extensor tendons.
- Triggering of fingers may occur because of nodules in the flexor tendonsheaths.
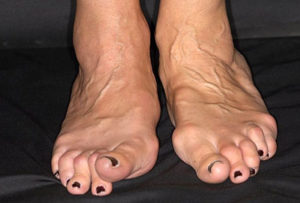
- Subluxation of the MTP joints of the feet may result in‘cock-up’ toe deformities, causing pain on weight-bearing onthe exposed MTP heads and the development of secondary adventitious bursae and callosities.
- In the hind foot, a valgusdeformityofthe calcaneus may be observed as the result of damage to the ankle and subtalar joints. This is often associated with loss of the longitudinal arch (flat foot) due to rupture of the tibialis posterior tendon.
- Prevalence: RA occurs in 0.5–1.0% of the population; women affected three times more often than men; prevalence increases with age, onset most frequent in fourth and fifth decades.2
Nodules
Rheumatoid nodules occur almost exclusively in RF- or ACPA positive patients, usually in extensor tendons. Theyare frequently asymptomatic but some may be complicated byulceration and secondary infection.1
Vasculitis
This is uncommon but may occur in seropositive patients. The presentation is with systemic symptoms, such as fatigue and feverand nail-fold infarcts. Rarely, cutaneous ulceration, skin necrosis and mesenteric, renal or coronary artery occlusion may occur.1
Ocular involvement
The most common symptom is dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitissicca) due to secondary Sjögren’s syndrome. Scleritisand peripheral ulcerative keratitis is uncommon but more serious and potentially sight-threatening complications that usually present with pain and redness.1
Serositis
Serositis is usually asymptomatic but may present with pleuralor pericardial pain and breathlessness. Pericardial effusion and constrictive pericarditis may rarely occur.1
Cardiac involvement
Heart block, cardiomyopathy, coronary artery occlusion andaortic regurgitation have all been reported but are rare.1
Pulmonary involvement
Pulmonary fibrosis may occur but is often asymptomatic. 1
Peripheral neuropathy
Entrapment neuropathies may result from compression byhypertrophied synovium or by joint subluxation. Median nerve compression is the most common and bilateral carpal tunnelsyndrome can occur as a presenting feature of RA. Other syndromes include ulnar nerve compression at the elbow or wrist, compression of the lateral popliteal nerve at the head of the fibula, and tarsal tunnel syndrome (entrapment of the posterior tibial nerve in the flexor retinaculum), which causes burning, tingling and numbness in the distal sole and toes. Diffuse symmetrical peripheral neuropathy and mononeuritis multiplexmay occur in patients with rheumatoid vasculitis.1
Spinal cord compression
This rare complication is caused by compression of the spinal cordfrom subluxation of the cervical spine at the atlanto-axial joint or at a subaxial level.
Other complications
Amyloidosis is a rare complication of long-standing disease that usually presents with nephrotic
syndrome. 1
Investigations
The diagnosis of RA is essentially clinical but investigations are useful in confirming the diagnosis and assessing disease activity.
- The ESR and CRP are usually raised but normal results do not exclude the diagnosis, especially if onlya few joints are involved.
- The main indication for n X-ray is in the assessment of patients with painful joints to determine whether significant structural damage has occurred.
- History and physical examination with careful examination of all joints.
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) is present in >66% of pts; its presence correlates with severe disease, nodules, extra-articular features.
- Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated protein (anti-CCP) have similar sensitivity but higher specificity than RF; may be most useful in early RA; presence most common in pts with aggressive disease with a tendency for developing bone erosions.
- Other laboratory data: CBC, ESR.
- Synovial fluid analysis: useful to rule out crystalline disease, infection.
- Radiographs: juxta-articular osteopenia, joint space narrowing, marginal erosions. CXR should be obtained.2
Management
The treatment goal is to suppress inflammation, control symptomsand prevent joint damage. When RA occurs in women of child-bearing age, additional considerations need to be taken into account.1
Goals: lessen pain, reduce inflammation, improve/maintain function, preventlong-term joint damage, control of systemic involvement. All RA therapies have individual toxicities, with many requiring pretreatment screening and monitoring.2
- Patient education on disease, joint protection.
- Physical and occupational therapy: strengthen periarticular muscles, consider assistive devices.
Pharmacological therapy
Various drugs from pain killers anti inflammatory to DMARD’s, Steroids all play a different role at different stages and are used in conventional therapy.
Non-pharmacological therapy
Physical and occupational therapy play important roles and it is vital for all patients to be assessed by an occupational therapist and physio therapist and the appropriate advice and treatment provided.1
Surgery
Synovectomy can be helpful in joints that have failed to respond adequately to systemic therapy and intra-articular injections. Joint replacement surgery may be required but the need for this has diminished over recent years, presumably as the result of more aggressive medical management.
HOMOEOPATHIC MANAGEMENT
Homoeopathy has great action on joints. Arthritis symptoms are well covered by many homoeopathic medicines. Aspects determining prognosis of cases for homeopathy are extent of disease, past history and other physical and mental health of patient. Rheumatoid Arthritis progression can be arrested to a good extent by constitutional or totality based homeopathic medicine. For acute episodes of pain there are many acute remedies which can be used for control of pain and inflammation. Regular use of constitutional remedy brings the ESR, CRP and RA factor values down. Right medicine can lead a patient to lead a pain free and normal life. It’s advisable to consult a registered homeopathic practitioner and take advice for a right homeopathic remedy. Homoeopathy has great action on joints. Arthritis symptoms are well covered by many homoeopathic medicines.
Few medicines useful in acute pain for RA are:
 BRYONIAAlba:
BRYONIAAlba:
The joints are affected producing articular rheumatism. The joints are sore & swollen. Pains are sharp; stitching in character.There is aggravation from slightest motion.
CAUSTICUM
There is stiffness of the joints. Restlessness of this remedy occurs at night. Pains impel constant motion, which does not relieve. Rheumatism caused by dry, cold, frosty air.
 CIMICIFUGARACEMOSA
CIMICIFUGARACEMOSA
Disagreeable sensation as of an electric shock in any part of body; pleurodynia of right side of chest; wandering rheumatic pains; affecting the belly of muscles; burning, cramping, stitching; excessive muscular soreness and numbness, (<) at night and in cold damp weather; articular rheumatism of lower limbs.
 DULCAMARA
DULCAMARA
When the weather suddenly changes to damp cold, or gets (<) on any little exposure to cold, or when rheumatism follows suppression of a cutaneous eruption. Sticking, drawing or tearing pains in limbs, with bloatedness of these parts and feeling as if they had gone to sleep;
 FERRUM METALLICUM
FERRUM METALLICUM
Neuralgic and rheumatic pains, (>) by slowly moving about at night; omodynia, especially left side (Sanguinaria, right deltoid), of a constant drawing, tearing, laming nature, (<) in bed; anaesthesia of affected parts, no swelling; face pale, flushing easily.
 KALIUM CARBONICUM
KALIUM CARBONICUM
Sharp stitching pain in lumbar region shooting down from the buttocks into the thighs; empty weak feeling in stomach before eating and bloatedness after; uneasy nervous feeling when hungry.
 KALMIA
KALMIA
It has wandering rheumatic pains. Hering says that the rheumatism of kalmia “generally goes from the upper to the lower parts”. Pains are worse when going to sleep.
 LITHIUM CARBONICUM
LITHIUM CARBONICUM
Chronic Cases: Swelling, tenderness, sometimes redness of last joints of fingers, with general puffiness of body and limbs; increase of bulk and with clumsiness in walking at night and weariness in standing; sometimes intense itching of side, feet and hands at night, without apparent cause; debility with or in consequence of joint affections.
 RANUNCULUS BULBOSUS
RANUNCULUS BULBOSUS
MUSCULAR RHEUMATISM, particularly in muscles about trunk, with much soreness to touch; muscles have a bruised feeling as if they had been pounded; INTERCOSTAL NEURALGIA AND RHEUMATISM; stitches about chest with every change of weather.
 RHUS TOXICODENDRON
RHUS TOXICODENDRON
Suitable to rheumatism affecting fibrous tissues, sheaths of muscles etc. Rheumatism from exposure to wet when overheated & perspiring. There is great restlessness & all symptoms are relieved by motion.
 RUTA GRAVEOLENS
RUTA GRAVEOLENS
RHEUMATISM OF RIGHT WRIST AND BOTH FEET; instep puffy; bruised feeling all over as from a blow, < in damp, cold weather, > from dry heat; sour sweat; stitches in small of back when sitting, stooping or walking, > by pressure and when lying down; pain in bones of feet, cannot step heavily on them < during rest and damp weather.
 ULMUS FULVA
ULMUS FULVA
Pain in small joints. Tingling as if asleep in lower extremities, aching in thighs.
References
- Ralston S.H., Penman I.D., Strachan M.W.J., Hobson R.P. Davidson’s, Principles and Practice of Medicine. 17thed. Edinburgh; New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1995. 1203p.
- Kasper D.L., Fauci A.S., Hauser S.L., Longo D.L., Jameson J.L., Loscalzo J. Harrison’s Manual of Medicine. 19th ed.United States: McGraw Hill; 2016, 1222p.
- Lilienthal, S. Homoeopathic therapeutics. Philadelphia: Boericke& Tafel; 1907
- healwithhomeopathy.co
Author:
Dr Geeta Rani Arora
BHMS, MD
Chief Consultant, Heal with Homeopathy
Director – Tintess Pvt.Ltd
Faculty -London College of Homeopathy
Former- Technical Head- B.Jain Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd
